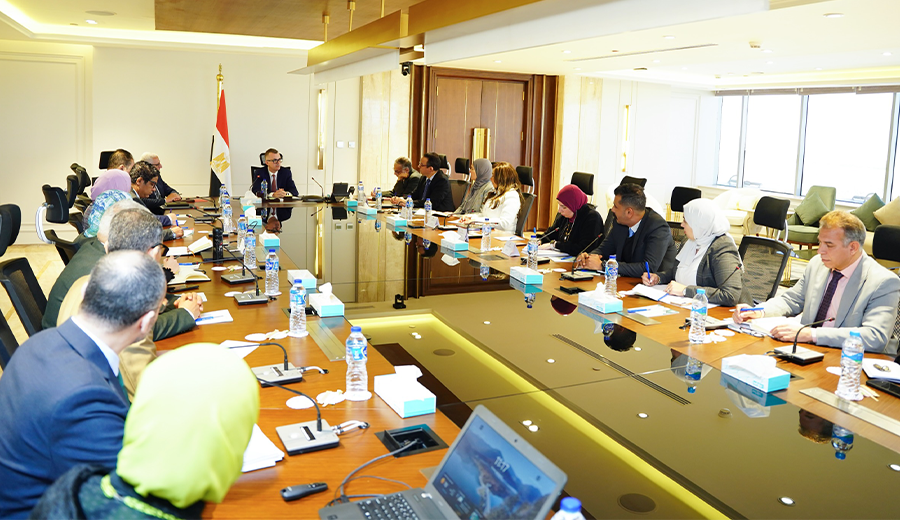
Following the Approval of a New Tranche Under the European Union Budget Support Mechanism … Dr. Rania Al-Mashat: $9.5 Billion in Concessional Financing Mobilized to Support the State Budget and Implement the National Structural Reforms Program (2023–2026)

15 January 2026
Following the Approval of a New Tranche Under the European Union Budget Support Mechanism
Dr. Rania Al-Mashat: $9.5 Billion in Concessional Financing Mobilized to Support the State Budget and Implement the National Structural Reforms Program (2023–2026)
Al-Mashat: Budget support financing is linked to comprehensive economic, social, and sectoral structural reforms within a clear, time-bound framework
More than 150 structural reform measures are being implemented to unlock financing across key sectors
Reforms aim to sustain momentum, unlock economic potential, and enhance competitiveness
Continued reforms remain essential to strengthening investor confidence and building on the economic recovery achieved in 2025
Concessional financing expands fiscal space and extends debt maturities at lower cost
H.E. Dr. Rania Al-Mashat, Minister of Planning, Economic
Development, and International Cooperation, announced that total concessional
development financing mobilized with multilateral and bilateral development
partners to support Egypt’s general budget reached approximately $9.5 billion
during the period 2023–2026.
This announcement follows the European Union’s approval of
the first tranche of the second phase of the Macro-Financial Assistance (MFA)
and Budget Support Mechanism, amounting to €1 billion.
Dr. Al-Mashat explained that this concessional financing
package is aligned with the implementation of the National Structural Reforms
Program, and is directly linked to a comprehensive set of economic, social, and
sectoral reforms implemented within a clear and time-bound framework. These
reforms are designed to sustain reform momentum, unlock the Egyptian economy’s
productive potential, and enhance overall competitiveness. She emphasized that
continued reform remains the only path to strengthening the confidence of the
business and investment community and consolidating the economic improvement
witnessed in 2025.
The Minister added that concessional financing represents
one of the least costly financing instruments available in international
markets, contributing to the expansion of fiscal space within the State budget,
the extension of debt maturities, and the reduction of short-term financing
pressures—consistent with national efforts to enhance debt sustainability and
improve debt management.
Dr. Al-Mashat noted that the concessional financing package
includes approximately $795 million in guarantees supporting the issuance of
Panda and Samurai bonds, comprising $200 million from the Asian Infrastructure
Investment Bank (AIIB) and $595 million from the African Development Bank
(AfDB). These guarantees enhance Egypt’s access to international capital
markets through lower-yield instruments that support sustainable development
projects and help diversify financing sources.
The overall financing package also includes:
● €4 billion
(approximately $5.7 billion) under the European Union’s MFA and Budget Support
Mechanism;
● $1.3
billion from the World Bank in Development Policy Financing and budget support
for the Universal Health Insurance System and the Takaful and Karama social
protection program;
● $557
million from the Japan International Cooperation Agency (JICA) to support the
Universal Health Insurance budget, private sector development, and economic
diversification;
● $221
million from the French Development Agency (AFD) as budget support for the
Universal Health Insurance Program;
● $300
million from the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank for Development Policy
Financing; and
● $572
million from the African Development Bank to support food security, economic
resilience, and private sector empowerment.
H.E. Dr. Rania Al-Mashat affirmed that all these financing
arrangements fall within the framework of implementing the National Structural
Reforms Program, which aims to formulate and execute reform policies in
coordination with relevant ministries and entities, in line with sectoral
strategies and within a clear timeline. The program is anchored around three
core objectives: strengthening macroeconomic stability, enhancing
competitiveness and improving the business environment, and supporting the
transition to a green economy.
She concluded by noting that the structural reform measures
linked specifically to budget support, totaling approximately 150 measures, are
part of a broader and comprehensive reform framework encompassing around 430
reform actions, many of which are already under implementation. These measures
are being executed by more than 40 national entities and span key areas
including tax reform, trade facilitation, public investment governance, social
protection, private sector participation, decent job creation, innovation and
start-ups, industrial competitiveness, and other priority sectors.